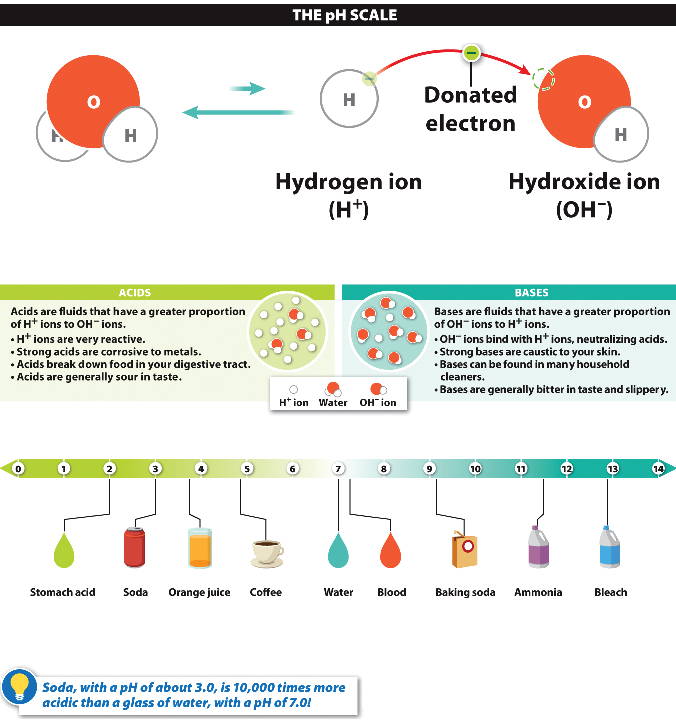
 pH scale
pH scale
Pure water
has the same concentration of hydrogen
and hydroxide
ions; this is 7
(neutral)
on a pH scale from 0 to 14.
If hydrogen
ion concentrations increase, the pH is lower than 7 and is an acid.
If hydrogen
ion concentrations decrease, the pH is greater than 7; it is a base.
An acidic
solution has a high concentration of hydrogen ions with a low pH.
A basic
(alkaline) solution has a low concentration of hydrogen ions with a high pH.

 The chemistry of biology
The chemistry of biology 
 The chemistry of biology
The chemistry of biology 