
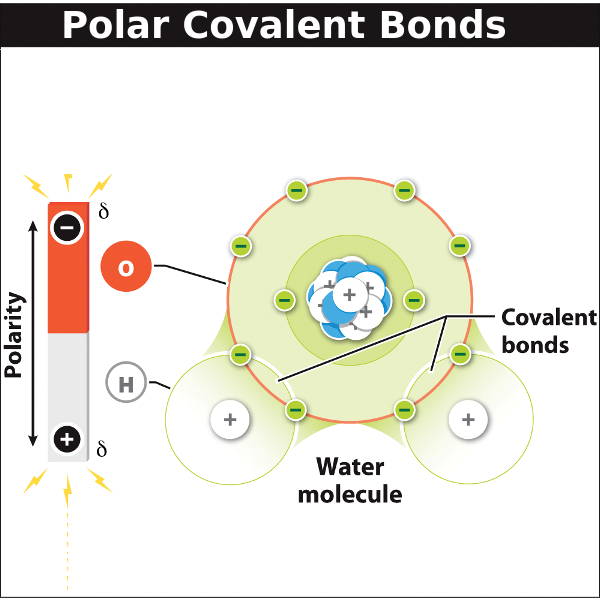
 A water molecule (H2O) has two polar covalent bonds:
one oxygen
atom forms a covalent bond with each of 2 hydrogen
atoms by sharing one electron pair with each hydrogen.
A water molecule (H2O) has two polar covalent bonds:
one oxygen
atom forms a covalent bond with each of 2 hydrogen
atoms by sharing one electron pair with each hydrogen.
The oxygen atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly than the hydrogen atoms; this unequal sharing of electrons makes these covalent bonds polar.
Water is a polar molecule with a partially (δ) positive "pole" at the hydrogen end and a partially (δ) negative "pole" at the oxygen end.