 Cells convert
energy from food into the energy storage molecule ATP
in a series of chemical reactions called cellular respiration.
Cells convert
energy from food into the energy storage molecule ATP
in a series of chemical reactions called cellular respiration.
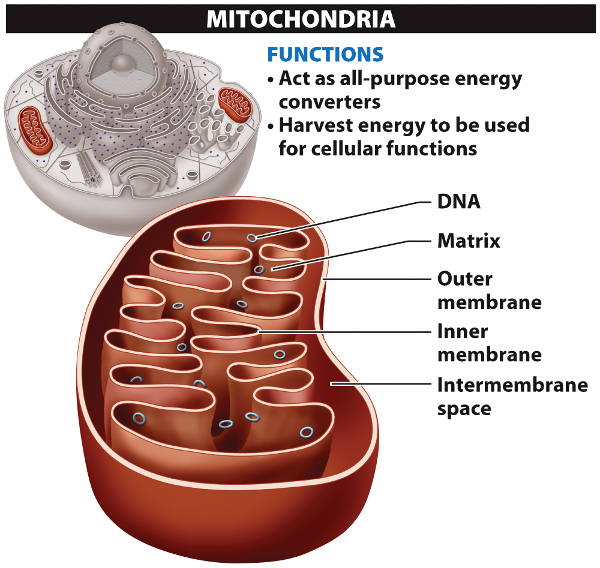
These reactions take place in mitochondria.
A mitochondrion has a double membrane where enzymes involved in cellular respiration
are embedded.
Liver and muscle cells that require a lot of energy
are rich in this organelle.
Note that mitochondria possess their own circular DNA.
 A tour of the cell
A tour of the cell 
 A tour of the cell
A tour of the cell 