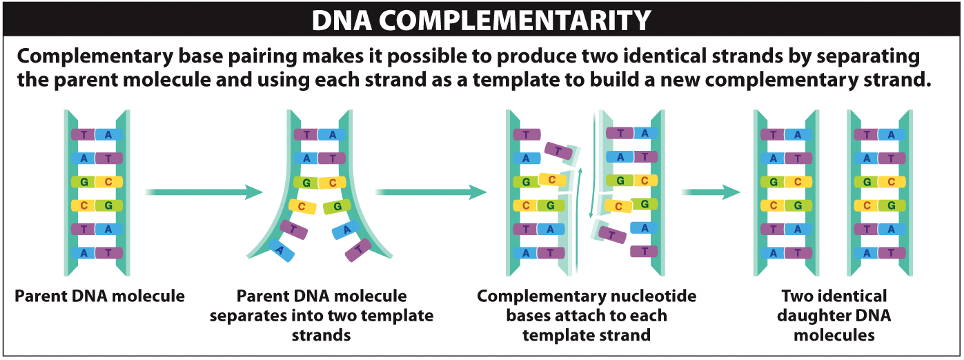
The two strands of a DNA double helix are complementary to each other.
The base on one strand always has the same pairing partner on the other,
following base-pairing rules:
- A pairs with T
- G pairs with C
To replicate DNA, the double helix is separated into single strands,
each of the parental
strands serving as a template to build a complementary strand, using the
enzyme
DNA polymerase.
At the end of this process, two identical daughter
double helixes are formed.
