
 Binary fission
Binary fission
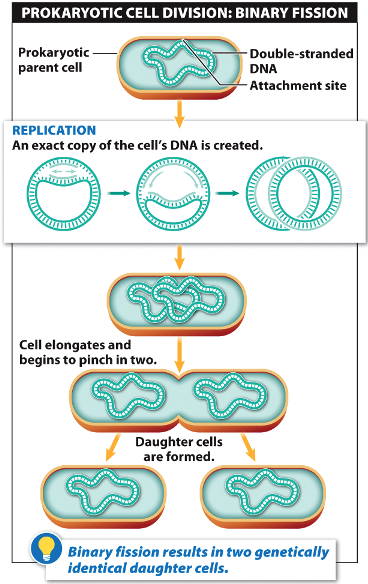
To reproduce, a prokaryotic cell initiates replication of its circular DNA, copying the DNA in both directions to yield two identical DNA molecules.
The cell elongates and grows a new membrane,
then undergoes binary fission and divides into two daughter
cells.
This form of asexual reproduction produces daughter
cells that are
genetically identical to the parent
cell.