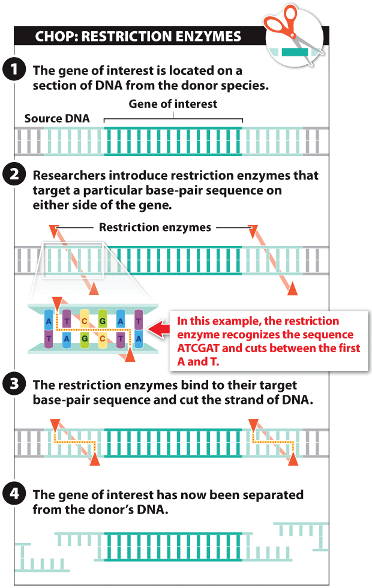
 Restriction enzymes can be used to isolate genes of interest.
Restriction enzymes can be used to isolate genes of interest.
- A gene of interest from a target organism is identified.
- A restriction enzyme can cut DNA
double helixes at specific restriction sites that contain a palindrome sequence.
- The restriction enzyme binds and cuts DNA
at the restriction sites.
- DNA fragments with complementary single-stranded ends are produced.
Some of these fragments contain the genes of interest.
After isolation, restriction fragments can reform double helixes with other sources of DNA
to produce recombinant DNA.
Review: 

 Restriction enzymes can be used to isolate genes of interest.
Restriction enzymes can be used to isolate genes of interest.