the 6-carbon glucose is split into 2 molecules of the 3-carbon pyruvate, yielding 2 ATP and NADH.
the pyruvate is broken down in the mitochondrion to form acetyl-coA, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2).
the acetyl-coA is broken down to release CO2 and yield more ATP, as well as NADH and FADH2.
NADH and FADH2 carry high-energy electrons that are used by proton pumps to produce ATP. Oxygen is needed to accept these electrons, releasing water.
Review:
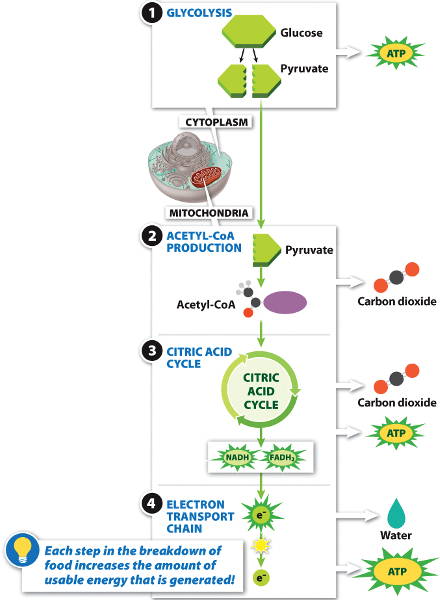 Cellular respiration steps
Cellular respiration steps
