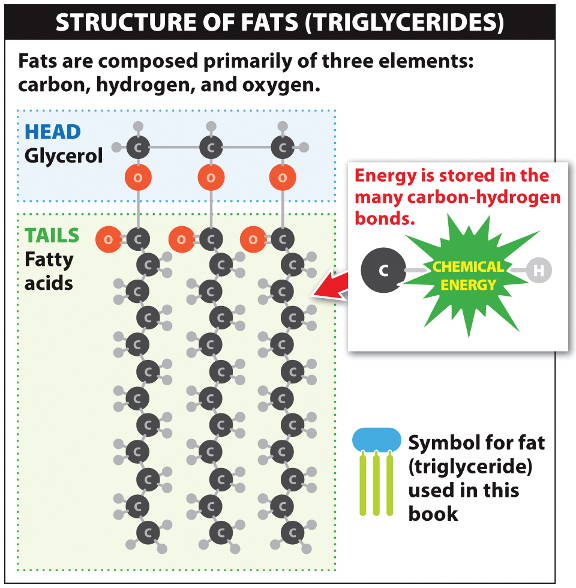
 Fat molecules are triglycerides,
each containing a glycerol head attached to 3 fatty acid tails.
Fat molecules are triglycerides,
each containing a glycerol head attached to 3 fatty acid tails.
A fatty acid is a long chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms (hydrocarbon).
The nonpolar hydrocarbons are hydrophobic ("afraid" of water) and are insoluble in water.
The dense covalent bonds make fats ideal for long-term energy storage; many animals develop a taste for sweet and fatty foods.